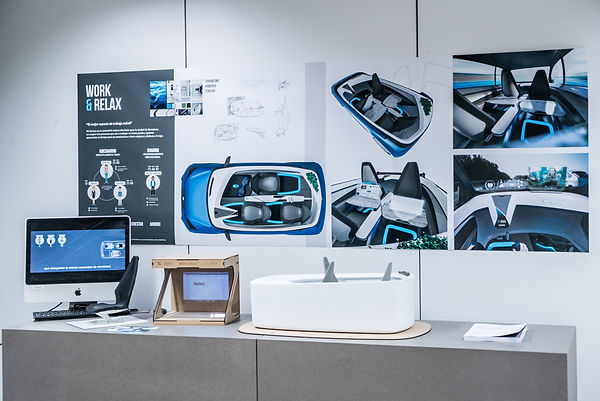
- Product Design Engineer -
DESIGN PROCESS
Following a good methodology in the design process is key for a successful result. Obviously, each product and client is different and the same steps can not always be followed, but the general methodology I usually use to design, based on Design Thinking, is explained below.



Most projects start with a briefing presented by a client or department of the same company. It is essential to understand the briefing perfectly in order to start the project with the correct approach and objective. In case of doubts about the content and limits of the briefing, you can respond with a debriefing to avoid any misunderstanding.
Brief presented by a client and debrief presented by students.
Once all the points of the briefing have been understood, it is important to make a timeline to meet the deadlines and work with objectives on a daily basis.
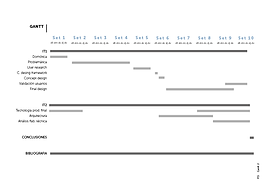


Timelines of different projects.
It is then when the research phase begins. For me, it is one of the most important parts of the design process. I usually divide it into two parts: the investigation concerning the product and the research referring to the users.
To design a product, a preliminary study must be done to know in which context will it be used, what elements will it coexist with, what its competence is, what technologies will it incorporate, which are the trends in the field, etc.

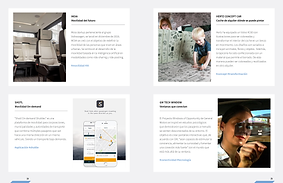
Benchmarking mobility services and technologies.


Positioning maps and opportunity map.



Trend study.
It is also necessary to understand the pains and needs of the target public to ensure the product fits in that sector of the population. To do this, different techniques are used such as interviews, surveys, observations, UX Cases, etc.





Different User personas and environment.
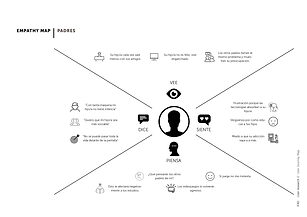
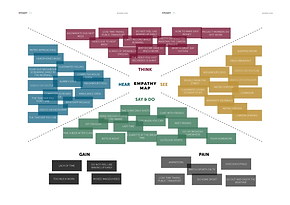
Empathy maps help understand the user.


In-situ interviews make the user feel more comfortable.

UX Cases consist of interacting with the users through different activities or stages to get the best of their thoughts.

Once the key insights are detected in the research phase, it is time to start ideating in consequence. Creating mind maps, mood panels, or user journeys can be a good source of inspiration and helps give high-quality results.

Insights searching on two different projects. Post-it maps make identifying insight much easier.

Mindmap as a source of inspiration.

You always have to be accompanied by paper and pen to draw and write down our ideas. Start exploring diverse random shapes that the product could have. From here we keep detailing and identifying the different pieces and materials.


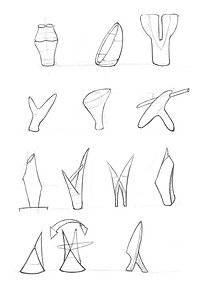




Different sketches done for University projects.

This process is complemented with prototyping and rapid-prototyping to understand the volume and ergonomics and be able to discard proposals.




Rapid prototypes to discart proposals and improve ergonomy and interaction.



1:1 Scale prototypes help understand volumes and distances in big products like a car.
Once the final proposal is selected, it is developed technically. For such, materials, finishes, joints, manufacturing processes, etc. are taken into account accompanied by the corresponding calculations to ensure its viability and efficiency.
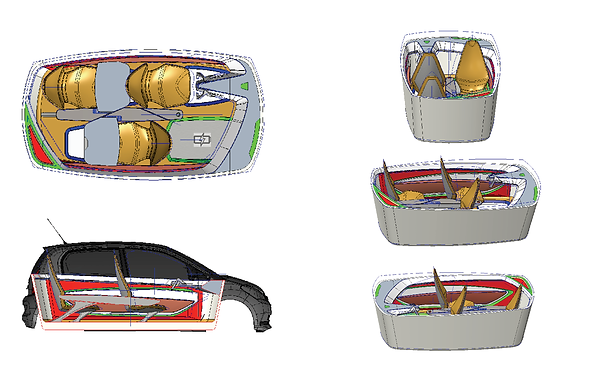
3D Modeling with an engineering Software.
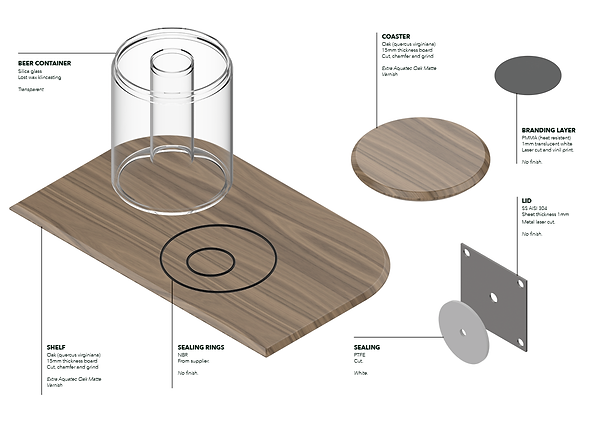
Selection of materials and finishes.


Ashby method is used to select precise materials with determined properties.

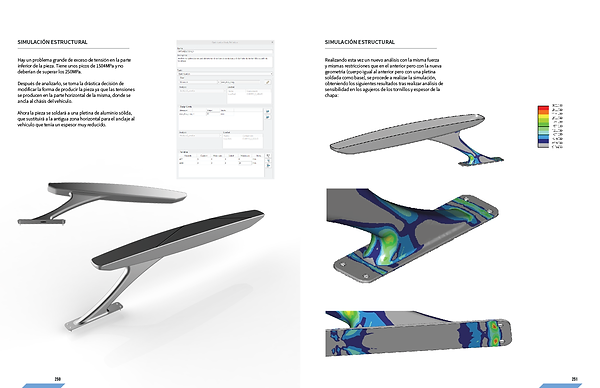
Structural Simulations are run to prove the product will support its efforts and work well under pressure.
Unmolding Simulations are run to prove the product can be injected into a mold.
Cost estimation is an important part of the design process.
Technical drawings are also made in order to allow the manufacturer to produce the parts correctly.
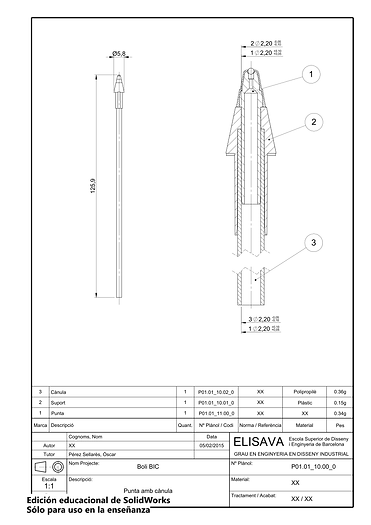-1.png)
-1.png)
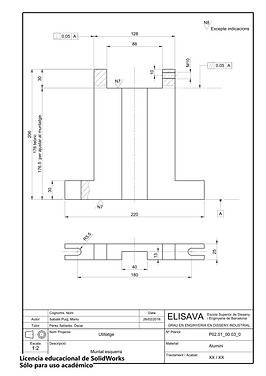%202-1.png)
Finally, we must know how to present and sell the result of this process to customers, and this is done with the help of explanatory renders, prototypes, graphic images or other techniques that manage to capture the customer's attention.






